Rolling contact bearings
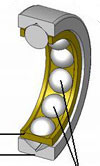 The terms rolling contact bearing, anti friction bearing and rolling element bearing are used to describe that class of bearing in which the main load is transferred through elements in rolling contact with each other. Friction in a rolling element bearing is present, but it is negligible when compared to the starting friction of a journal type bearing. The load, bearing speed and the viscosity of the lubrication all affect the friction within the bearing. Although it is not technically correct to refer to this type of bearing as anti friction, it is a name that is in constant use.
The terms rolling contact bearing, anti friction bearing and rolling element bearing are used to describe that class of bearing in which the main load is transferred through elements in rolling contact with each other. Friction in a rolling element bearing is present, but it is negligible when compared to the starting friction of a journal type bearing. The load, bearing speed and the viscosity of the lubrication all affect the friction within the bearing. Although it is not technically correct to refer to this type of bearing as anti friction, it is a name that is in constant use.
Bearings reduce friction by providing smooth/polished metal balls or rollers, and a smooth/polished inner and outer metal surface for the balls to roll against. These balls or rollers carry the load, allowing the device to rotate smoothly.
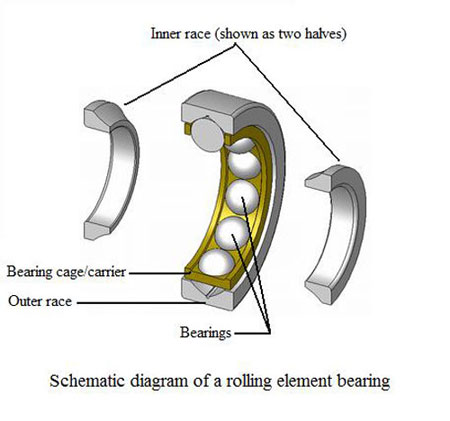
In general a rolling element bearing is a bearing which carries a load by placing round elements between two surfaces. These surfaces are referred to as the inner race and the outer race. The relative motion of the races causes the bearing elements to roll, with little or no sliding. Bearings are normally selected on the basis of a requirement to carry a given load for a given period of time. Rolling contact bearings are designed to carry pure radial loads, pure axial loads or a combination of the two.
The bearing designer is confronted with the problems of designing a group of elements which make up a rolling element bearing. Parameters such as fatigue, loading, heat, corrosion resistance and lubrication, to name but a few, must be considered. There are many types of rolling element bearings, each designed to carry a specific kind of load. Each of the different types of bearing contain either a ball bearing, a roller bearing or a needle type bearing. A needle bearing is an elongated roller bearing.
Rolling-element bearings may rotate at over 100,000 rpm. Maximum rolling element bearing speeds may be specified in 'DN', which is the product of the diameter (in mm) and the maximum revolutions per minute (rpm).
There are also many material issues for bearings. For example, a harder material may be more durable against abrasion but more likely to suffer fatigue fracture. Therefore, the material varies with the application, and whilst steel is the most common for rolling element bearings, plastics and ceramics are also in use.
A bearing can last indefinitely; longer than the life of the machine, if it is kept clean, lubricated, and operated within its load rating. Also, every effort needs to be made during manufacture to make sure the bearing materials are sufficiently free of microscopic defects. Note, that cooling, lubrication, and sealing are also important parts of bearing design.
The operating environment and servicing needs must also be considered in bearing design. Some bearing assemblies require routine addition of lubricants, while others are factory sealed, requiring no further maintenance for the life of the bearing or assembly. Although seals are appealing, they increase bearing friction, and a permanently sealed bearing may have the lubricant contaminated by hard particles, due to bearing wear, which will abrade the bearing.
Fig. 1 - Schematic diagram of a rolling element bearing.
Written by Eric Smart